PolyPico dispensing technology has been successfully used in an experiment to Decipher the degradation of last resort antibiotics by beta-lactamases
The experiment used drop-on-drop time-resolved serial femtosecond crystallography and it was conducted on the Macromolecular Femtosecond Crystallography (MFX) instrument, Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS), Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC) National Accelerator Laboratory, California, USA.
PolyPico’s precision dispensing technology played a critical role in a groundbreaking experiment that aimed to uncover how beta-lactamases—a class of enzymes responsible for antibiotic resistance—degrade last-resort antibiotics. This experiment holds immense importance for understanding mechanisms behind antimicrobial resistance, especially as these enzymes continue to compromise our most powerful treatments.
The study utilized drop-on-drop time-resolved serial femtosecond crystallography, a powerful technique that captures rapid molecular changes at atomic resolution. This approach allowed scientists to observe the degradation process in real time, with remarkable precision.
The experiment was conducted at the Macromolecular Femtosecond Crystallography (MFX) instrument at the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS), located within the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC) National Accelerator Laboratory in California, USA. LCLS is one of the world’s most advanced X-ray free-electron lasers (XFELs), capable of producing ultra-bright, ultra-short X-ray pulses. These pulses allow researchers to “freeze” biochemical reactions in motion, essentially capturing molecular events that occur in femtoseconds (one quadrillionth of a second).
About the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS)
LCLS is a world-leading facility operated by SLAC and supported by the U.S. Department of Energy. It provides researchers from around the globe access to intense X-ray pulses that can reveal the structure and dynamics of complex molecules with extraordinary clarity. Applications range from drug development and materials science to studying virus behavior and catalytic reactions. The facility recently underwent upgrades (LCLS-II) to increase its pulse repetition rate and overall capabilities, making it even more powerful for time-resolved experiments like the one described here.
The integration of PolyPico’s high-precision microdispensing technology with LCLS’s advanced instrumentation showcases how collaborative innovation is pushing the boundaries of structural biology and antibiotic research. This type of research is critical as scientists race to stay ahead of the growing threat of drug-resistant bacteria.
Read more about Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS)
For other use cases, please refer to the following:
PolyPico To Demo Micro Drop Dispensing Technology at UCC
Harvard Medical School uses PolyPico technology

Related Posts
Revolutionising Fluid Dispensing with Microdrop Technology – EU Startup News Feature

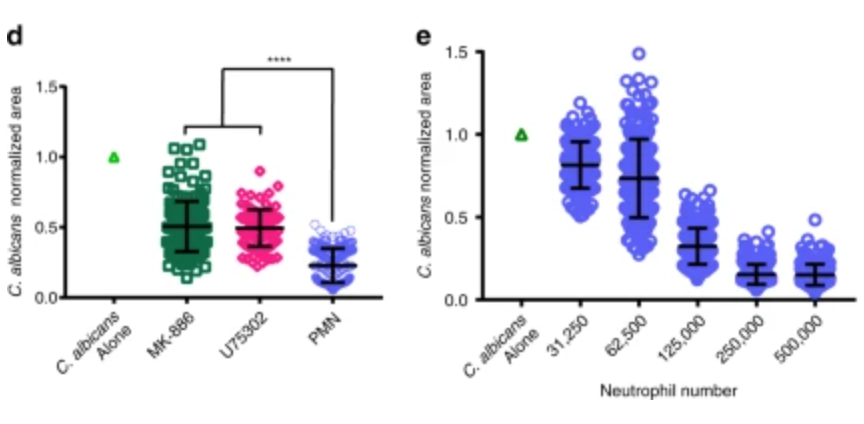
Polypico systems, used in breakthrough Neutrophil research